Add/Modify Security Policy
This function helps you add/modify the security policy.
Operation Procedure
- Enter the Security Policy Management page.
Approach 1: Select the User tab, click User Security Policy/Quick Start and then click Security Policy.
Approach 2: Select the User tab, and then in the navigation tree click User Security Policy/Security Policy.
- Click Add to enter the Add Security Policy page, or click the
 link to enter the Modify Security Policy page.
link to enter the Modify Security Policy page.
- Type the basic information of the security policy, isolation mode, configure the URL control,
anti-virus software control, anti-spyware software control, firewall software control, anti-phishing software control, hard disk encryption software control, software control group, patching software control, Windows patch control, registry control, share control, asset registration status check, Windows System Settings, periodic check parameters, and MDM collaboration policy.
- Click OK.
Parameters
Basic Information
- Monitor in Real Time: Specifies whether to enable real-time monitoring of terminals. These items support real-time monitoring: anti-virus software, anti-spyware software, firewall software, anti-phishing software, hard disk encryption software, PC software control group, registry and terminal share.
- Process After: When the terminal fails the real-time monitoring, the system waits for a period specified by this field before isolating or kicking out the user. If the value is 0, the system isolations or kicks out the user immediately. This option is available only when the Monitor in Real Time check box is selected.
- Set as Default Policy for Roaming Users: Apply the security policy to users that roam to the local domain. Only identity authentication is performed for roaming users if no default security policy is configured for them.In hierarchical node management,the default policy for roaming users will be issued automatically, and no associated access service is required.
- Service Group: Specifies the service group to which the current security policy belongs. Authorized operators can add a security policy to their associated service groups.
Isolation Mode
- The isolation mode can be Deploy IPv4 ACLs to Access Device, Deploy IPv6 ACLs to Access Device, Deploy ACLs to iNode Client, Deploy VLANs to Access Device, or Deploy User Groups to Access Device. To deploy IPv4 ACLs to the access device or ACLs to the iNode client, you can manually enter the ACL numbers or select them from the list. To deploy IPv6 ACLs to the access device, you can only manually enter the ACL numbers. If you select the Deploy ACLs to Access Device option,use one of the following methods:(1)Enter an ACL string. Use this method for the following device vendors: HP, 3Com, Cisco, and Huawei. For information about configuring an ACL, see the ACL management help. When an HP A-Series device is used, the string must be an ACL number. When other device is used, the string can be an ACL number or name. Make sure the ACL number and rules that are identified by the string are already configured on the device. (2)Select an ACL from the list. This function requires the ACL management module to be installed and deployed. The list includes all ACL resources configured in ACL management.This method does not require the ACL rules to be configured on the device in advance.Specially, HP ProCurve devices also support the ACL rules configured in Access ACL. HP ProCurve devices are of HP(General) type on the User> User Access Policy > Access Device Management > Access Device page. Support for this method depends on the device models. For more information, see the ACL management specifications.If you select the Deploy ACLs to iNode Client option, you can select a client ACL to be deployed to the iNode client. The client ACL is configured in Client ACL Management. If you select the Deploy VLANs to Access Device option, configure the VLAN ID or name that is configured on the access device. If you select the Deploy User Groups to Access Device option, EAD deploys user groups to the access device. Multiple user groups must be separated by semicolon. This function takes effect only when EAD works with SSL VPN devices.
- Two kinds of ACLs can be deployed:
- Isolation ACL: Controls the access range of a user failing the security authentication.
- Security ACL: Controls the access range of a user passing the security authentication.
- Two kinds of VLANs can be deployed:
- Isolation VLAN: The VLAN used by a user failing the security authentication.
- Security VLAN: The VLAN used by a user passing the security authentication.
- Two kinds of User Groups can be deployed:
- Isolation User Group: User group for users who failed the security check.
- Security User Group: User group for users who have passed the security check.
URL Control
- Enable URL Access Control: Checks whether the URLs accessed by the user comply with the URL control policy. If yes, the user can normally access the URLs; if not, the iNode client will forbid the access to the URL, and displays an error prompt. To select the Check Hosts File option, you must select this option.The IP addresses in URLs must be IPv4 addresses. URLs containing IPv6 addresses are not supported.
- Check Hosts File: Checks the hosts file configuration on the user terminals. If the hosts file contains an IP address that does not exist in the list, the iNode client will force the user to log out.
Anti-Virus Software Control
- Check Anti-Virus Software: Checks whether the anti-virus software is installed on a user terminal and satisfies the terminal security software control requirements.
- Server Address: If a terminal fails the check, the iNode client prompts the user to make remediation from the update server if you specify the server's IP address in the Server Address text box.
Anti-Spyware Software Control
- Check Anti-Spyware Software: Checks whether the anti-spyware software is installed on a user terminal and satisfies the terminal security software control requirements.
- Server Address: If a terminal fails the check, the iNode client prompts the user to make remediation from the update server if you specify the server's IP address in the Server Address text box.
Firewall Software Control
- Check Firewall Software: Checks whether the firewall software is installed on a user terminal and satisfies the terminal security software control requirements.
- Server Address: If a terminal fails the check, the iNode client prompts the user to make remediation from the update server if you specify the server's IP address in the Server Address text box.
Anti-Phishing Software Control
- Check Anti-Phishing Software: Checks whether the anti-phishing software is installed on a user terminal and satisfies the terminal security software control requirements.
- Server Address: If a terminal fails the check, the iNode client prompts the user to make remediation from the update server if you specify the server's IP address in the Server Address text box.
Hard Disk Encryption Software Control
- Check Hard Disk Encryption Software: Checks whether the hard disk encryption software is installed on a user terminal and satisfies the terminal security software control requirements.
- Server Address: If a terminal fails the check, the iNode client prompts the user to make remediation from the update server if you specify the server's IP address in the Server Address text box.
PC Software Control
- Check PC software: Checks software installation, running processes, service start, or file existence on the iNode client PC against the PC software control configurations. Options in the Check Type dropdown list include Installation Forbidden,Installation Required, and Only Installation Allowed for a software-type group, Running Required and Running Forbidden for a process-type group, Started Required and Started Forbidden for a service-type group, Existence Required and Existence Forbidden for a file-type group.
- Server Address:Specifies the server that provides software update services. When software on the endpoint does not meet the security requirements, the iNode client requires the user to connect to this server for remediation. The server does not fix user endpoints that do not meet the process, server, or file check requirements.
- Security Threshold:EAD counts security check failures for a user. When the count reaches the security threshold, EAD takes the action according to the security level, for example, logs out or isolates the user. When the user passes the security check, EAD clears the counter for the user.If the value is set to 0, EAD immediately takes the action according to the mode configured for the security level, for example, logs out or isolates the user. EAD counts security check failures in endpoint authentication or reauthentication. Security violations in realtime monitoring are not counted.
Patching Software Control
- Check Patching Software: Checks the installation and running status of the patching software on a user terminal according to the patching software control configuration.
Windows Patch Control
- Check Windows Updates: You can perform Windows update check manually or through the remote WSUS server or the locally associated WSUS server.
- When you select the manual check, you must configure Windows update information that is required for user authentication.
- When you select to check updates through the remote WSUS server, you must configure Windows updates to be checked on the WSUS server. For more information, see the typical application of Collaboration Application with Microsoft WSUS.
- When you select to check updates through the locally associated WSUS server, you must configure WSUS server information in INC to manage the update check and installation on computers.
- Days Since Last Patch Installation: Enables the system to examine the most recent patch installation time of the endpoint. If the endpoint has not install patches within the specified period, the endpoint fails the check. The system takes an action according the security level setting, such as logging out or isolating the endpoint.
- Server Address: Microsoft WSUS patch server or SMS server address in the format http://host:port or https://host:port. The host string indicates an IP address, computer name, or full computer name with a domain name. If you do not specify the protocol, the system automatically adds "http://" to the address during communication. You can remove the ":port" string to use the default port setting, which is HTTP 80 or HTTP 8443. Valid server addresses would be wsus.contoso.com, 10.153.128.57:8080, http://wsus, and https://wsus.contoso.com:8443, where wsus is a computer name and contoso.com is a domain name.
- Patch Server Address: IP address of the server saving the patches. If you select the Check Manually option and configure the patch server address, when a terminal user fails to pass the patch check, the client will prompt the user to access the patch server to install patches.
- Flexible Patching: When the users are performing authentication, if the patches are automatically installed for these users at the same time, the patch server will be overloaded. With flexible patching enabled for an area, UAM organizes the users to be patched according to the security policy in the area into groups, and distributes the patch installation work across a week. To avoid the problem that some users do not install patches for a long time because the users do not log on when they should be patched, the policy server forces each user whose patch interval exceeds 21 days to perform patch check even if the user logs on when they should not be patched. After the flexible patching is performed for an area, the patch check interval setting in the EAD system parameters does not take effect for the area.
Registry Control
- Check Registry: Checks the items defined in the registry monitoring policies. You can specify which registry monitoring policies are to be used for checking.
Share Control
- Check Share: Checks the item defined in the terminal share policy. You can specify which terminal share policy is to be used for checking.
Asset Registration Status Check
- Check Asset Registration Status: Checks the registration status of assets. Only assets registered with the DAM component can pass this check. The option is available only if the DAM component is installed.
- Grace Days for Unregistered Assets: Specify a grace period in days for unregistered assets. The value must be an integer in the range of 0 to 999. A value of 0 indicates that the system does not have a grace days for unregistered assets. During the grace period, the system allows an unregistered asset to pass the security check and sends a daily reminder for asset registration. If the asset is still unregistered at the expiration of the grace period, the asset user will be isolated or kicked out, depending on the security level settings.
Windows System Settings
- Check Windows System Restore: Check whether Windows system restore is enabled on the endpoint.
- Enable Data Execution Prevention: Checks whether data execution prevention is enabled. If the feature is disabled, the iNode client automatically enables the feature and the change takes effect at the next startup of Windows. The change does not require an immediate operating system restart because this is not an emergent security issue.
- Disable Guest Account: Checks whether the guest account is disabled. If the guest account is enabled, EAD automatically disables the account.
Periodic Check
- Traffic Control: Specifies the traffic monitoring policy for the security policy to use.
- Check Operating System Password: Specifies whether to check the password used to log in to the operating system.
- Check All Local Users: Select this option to check the OS passwords for all the local users.
- Check Dictionary Files Only for INC: Specifies dictionary files to be checked. When this parameter is selected, iNode checks the dictionary files only in INC. When this parameter is not selected, iNode checks the dictionary files both in INC and iNode.
- Add to Security Check: Select this option to check the OS password for both security check and periodic check. Do not select this option if large dictionaries are used for password check. Otherwise, security check can take a long time.
External Storage Device Control
- Read-Only: If this option is selected, endpoints that use the security policy can read data from external storage devices but cannot write data to storage devices.
Screen Saver Check
- Check Screen Saver: Checks whether the screen saver is enabled. If the screen saver is enabled, the check passes.
- Check Password: Checks whether the screen saver password is set. If the screen saver password is set, the check passes.
- Max. Screen Saver Wait Time: Sets the maximum screen saver wait time. If the wait time set by the user exceeds this value, the check fails.
IPsec Policy Configuration
- Deploy IPsec Configuration: Applies the IPsec configuration to terminals using this security policy.
Firewall Policy
- Deploy Firewall Policy:Specify whether or not to deploy the firewall policy.
- Firewall:Specify whether or not to enable the firewall.
MDM Collaboration Policy
- Check MDM Collaboration Policy Configuration: Check whether the user terminal settings comply with the MDM collaboration policy. The MDM collaboration policy is displayed only when the MDM collaboration configuration is enabled on User Access Policy >> Service Parameters >> Vendor Configuration page .
Precautions
- The security policy name and the service group to which the security policy belongs are not editable.
- You have two options to deploy an ACL to access devices, For Non-HP ProCurve and For HP ProCurve. To deploy the ACL to a non-HP ProCurve device, you can either manually enter the ACL number or select the ACL identifier and rule set from the list. Make sure that the ACL number you enter already exists on the access device. Otherwise, you might fail to deploy the ACL. The ACL lists appear only when the ACL Manager component is present. To deploy the ACL to an HP ProCurve device, select the ACL from the list. Configure the ACL rules of the ACL on the Access ACL Policy Management page.
- To deploy an ACL to the iNode client, select the ACL from the list. Configure the ACL rules of the ACL on the Client ACL Management page.
- INC EAD assigns only VLAN IDs or VLAN names to access devices. These VLANs must be preconfigured on the access devices.
- You can input an IP address or a host name in the Server Address text boxes for the patch server, anti-virus software server, anti-spyware software server, firewall software server, anti-phishing software server, and hard disk encryption software server.
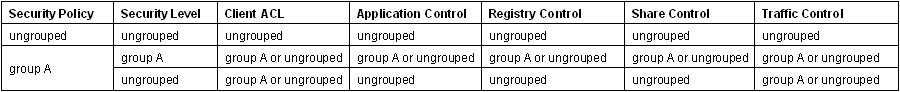
- When configuring a security policy, note that which security levels and related policies are available depends on the service group you select. The following table provides the restriction details:

- The default security policy for roaming users is used for security authentication of local roaming users. If no security policy is configured as the default security policy for roaming users, only identity authentication will be performed for local roaming users.
- For a user who has passed the identity authentication but has not passed the security check, EAD determines to deploy either the security ACL / VLAN or the isolation ACL / VLAN by the Action After parameter in the security level configuration. If the parameter is not configured or is set to 0, EAD deploys the isolation ACL / VLAN. If the parameter is set to a positive value, EAD deploys the security ACL / VLAN. If the user passes the security check, EAD deploys the security ACL / VLAN to the device. If the user fails the security check, EAD deploys the isolation ACL / VLAN to the device. EAD does not deploy the security ACL / VLAN or isolation ACL / VLAN if the same ACL / VLAN is already deployed to the device. During real-time monitoring, if a user does not comply with the security policy requirements, EAD waits the period specified by the Process After parameter of the security policy before it deploys the isolation ACL / VLAN to the device. EAD does not deploy the ACL / VLAN if the ACL / VLAN is already deployed to the device.
- When configuring an software control group group of software type, follow these guidelines: 1) After configuring a software control group of the Installed Allowed type, no more software control group can be configured. 2) After configuring a software control group of the Installed Forbidden or Installed Required type, you can continue to configure software control groups other than the Installed Allowed type. 3) To deploy a security policy successfully, make sure the total number of software entries in the bound software control groups does not exceed 10000.
- When applying the security policy of a parent node to a child node, the software control group configuration of the parent security policy, if any, takes effect and some software control group configuration of the child node security policy does not take effect. The following are the detailed rules: 1) If the security policy of the parent node deploys a software control group of the Installed Allowed type, the software control group configuration in the child node security policy does not take effect. 2) If the security policy of the parent node deploys a software control group of the Installed Forbidded or Installed Required type, the software control group of the Installed Allowed type in the child node security policy does not take effect. 3) If the security policy of the parent node does not deploy a software control group, the software control group specified in the child node security policy is not affected.
- The URL control policy feature is available for only the Windows iNode clients.
- Make sure that the target access device supports the ACL/VLAN/User Group deployment feature.
- When using the default roaming security policy, security logs and endpoint security assessment results will not be recorded.

